Whether the product is web hosting or internet service, one of the biggest selling points is speed. Marketers use terms like “blazing fast internet” and “unlimited bandwidth” to tout their superiority over the competition. But, what do metrics like bandwidth, latency, and throughput really mean, and how do they affect important issues like user experience (UX) and website performance?
The Need for Speed

It’s difficult to discern which came first, the customer demand for speed or the service provider’s insistence that you need more of it. What we do know is it’s a factor in everything from bounce rates to SEO evaluation. Studies show that the average consumer will abandon a mobile website if the page doesn’t load within three seconds, and how long it takes your landing page to load will affect how Google ranks your site both directly and indirectly.
The speed of an internet connection doesn’t just play a factor in the buyer’s journey or UX while surfing. Advanced graphics require a certain amount of bandwidth, speed, and reliability for users to get the full gaming experience. The three factors that relate to the potential and actual speed of an internet connection are bandwidth, latency, and throughput. They’re interrelated, and the rate of anyone affects the others in several ways.
If you’re confused, you’re not alone. Read on to learn more about these metrics and how they affect internet use and enjoyment on both sides of the browser.
Recommended for you: Top 8 Benefits of Cutting-Edge Fiber Optic Internet Technology.
Bandwidth, Latency, and Throughout, Oh, My!
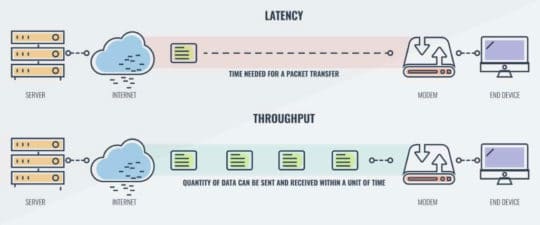
Bandwidth, Latency, and Throughput, these three terms relate to how much data your connection is capable of transferring, how much it actually transfers, and the speed at which it travels over a given distance or period of time. Both the terms and their practical applications are interrelated with each other and determine how well a website presents information within the shortest possible amount of time, regardless of distance from the browser to the server.
Image source: www.comparitech.com.
How Does Bandwidth Work?
Bandwidth basically refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred through your network line within a given period of time. However, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll be able to reach that capacity.
It also means something different to the average internet user than it does to a website owner.
In terms of surfing the internet, your service provider will tell you that you’re getting a certain level of bandwidth through their service. The more bandwidth you have available, the faster your connection and download speeds, in theory.
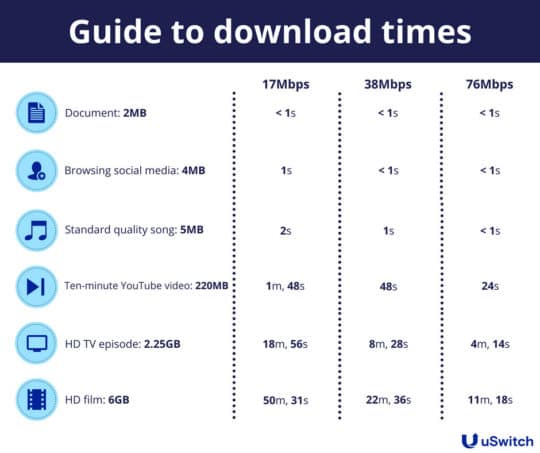
For example, the typical data plan on your mobile or home internet service might offer a plan that gives you an internet speed of 1000 Mbps (megabits per second), which means that your network is capable of transferring 125 megabytes of data through your connection in a given time. Megabits are the data transfer speed and megabytes relate to the file size.
Image source: www.uswitch.com.
Modern internet connectivity is brought to you over various types of high-speed broadband networks, which make high bandwidth possible.
These include:
- Direct Subscriber Lines (DSL).
- Cable modems.
- Satellite.
- Fiber optic networks.
- Wireless routers.
When you build a website, you choose a hosting platform to make your site available to the public. The bandwidth offered through your hosting plan relates to how much traffic your server can bear at any given time. If your bandwidth is limited, heavy traffic or unoptimized pages will eat resources and affect how your site loads and performs for your visitors. Poor performance means unsatisfied customers, loss of business, and lower page ranks on Google.
When you’re in the market for website hosting plans, you may see incentives like “unmetered” or “unlimited” bandwidth. These are relatively meaningless marketing terms. Each time someone accesses your website, they’re using available resources. When your hosting company gives you unlimited bandwidth, they’re allowing you to have as much traffic – or use as many resources – as needed without charging extra when you reach a certain predetermined limit. Unmetered bandwidth simply means that they aren’t measuring the number of resources you’re using.
You can determine how much bandwidth is sufficient by answering the following questions:
- What is your network being used for?
- How many people will be using your network?
- Are your applications cloud-based or stored in a data center?
- How much traffic will you generate at your busiest time?
- Will you be installing a VPN or using encryption?
- How many resources will you need for core applications?
- What type of applications will you be running? For example, the video uses more bandwidth than files that are mainly text.
Other ways to get the full amount of bandwidth you’re paying for include:
- Using a proxy cache.
- Monitoring your system for malware.
- Switching to a different wireless channel.
- Using a wired connection.
- Managing streaming content.
- Setting your router to auto-reset when not in use.
You may like: NordVPN vs SiteLock VPN – Which One is Best for You?
How Throughput Measures Performance
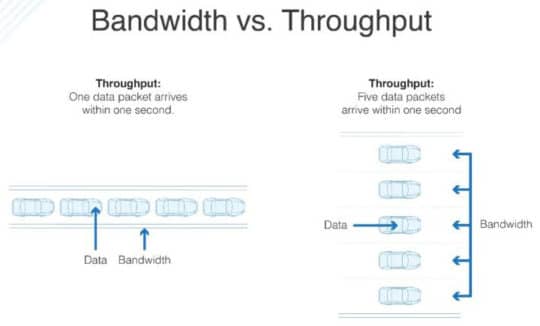
If bandwidth describes maximum capacity, throughput rates measure how much data is actually transferred through your connection. When a browser makes a request to the server, packets of data are sent back to the user in response. These packets are information in the form of written content, images, and video.
When the server is unable to handle these packets in a timely manner or they’re lost in transit, it lowers the throughput rate and performance suffers. This, in turn, affects latency, which we’ll get to in a minute.
Image source: www.dnsstuff.com.
High performing websites have higher throughput in relation to the available bandwidth, meaning you’re able to leverage your overall data transfer capacity and latency. Knowing your bandwidth and throughput will help you evaluate your website’s performance.
What affects throughput?
Factors such as:
- Network congestion due to high traffic.
- Faulty or outdated routers.
- Packet loss.
What is Latency?
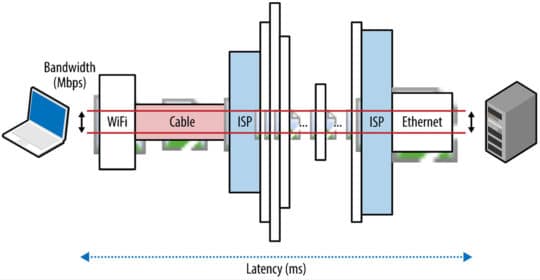
Latency is the amount of time it takes data to travel from point A to Point B and back again. In general, packets moving between a browser in New York and a server in California will take less time than the same amount of data traveling from New York to London or India and back.
Image source: hpbn.co.
However, it isn’t just distance that affects latency.
There are several different types of delays that contribute to latency, and each affects the speed in a different way.
- Transmission delay: This relates to the transfer time for all of the packet bits to get pushed into the link. This is the function of the packet length and the link’s data rate.
- Propagation delay: How long it takes the signal to propagate from when a message travels from sender to receiver.
- Queuing delay: These delays relate to how much time a packet sits in the queue until there are enough resources available to process it.
- Processing delay: Processing delays relate to the amount of time it takes to process components like the packet headers, determine the packet destination, and check for errors at the bit level.
However, it’s important to note the unit of measurement for latency, which is different for network and non-network performance. When referring to latency, network units are measured in bits per second (bps), while non-network units are designated in bytes per second (Bps). There are eight bits in a byte. So, a 10MB file on a 1Mbps wire will take 80 seconds to transfer.
You can extrapolate this as the basis to calculate any transfer rate. Latency can also be measured with a tool called Traceroute.
Speed and the Problem of Unintended Consequences
In an effort to provide users with the highest rate of data transfer possible, manufacturers began creating routers with large incoming buffers. The idea was to prevent packet dropping at all costs, but it broke TCP’s avoidance mechanisms. This led to a problem called buffer bloat. Fortunately, this issue has since been addressed through an active queue management algorithm.
If you want to minimize latency, it’s necessary to optimize throughput. You can achieve this by:
- Using a content delivery network (CDN) to shorten the distance from the browser to the server.
- Gaining better insight into how the user connects with your website.
- Monitoring network bottlenecks and determining the source.
- Utilizing an effective SSL cert to verify all website data is authenticated.
Using Throughput to Troubleshoot Your Network

You can use throughput in relation to bandwidth to detect a problem with network performance. Because low throughput means that you’re wasting the potential of your connection.
You can avoid network congestion and conserve resources by optimizing throughput. The main way to do this is by reducing latency by following the above recommendations.
It’s also important to:
- Keep hardware, firmware, and applications up to date.
- Use the latest version of your operating system.
- Remove or disable apps that use too many resources and memory.
- Identify and correct issues that affect latency.
“You don’t have to wait for your traffic to suffer, Google to punish you, or customers to give you bad reviews when you optimize your network capabilities and test your networks regularly for issues. Google developers have created some great developer tools, and most of them are free.” – as mentioned by InternetAdvisor in their recent press release.
You can check your mobile performance with this mobile speed test, and Pingdom has a great tool for testing website page loads on any platform.
You may also like: How Network Security Can Help Avoid IoT Device Hacking?
Final Thoughts

Our goal is to provide you with the most comprehensive, current information available about telecommunications and technology so that you can make the best decisions about the services you need. Hopefully, you have understood what the terms bandwidth, latency, and throughput actually mean. Now you’re knowledgable with more information about how to determine the internet speeds and data transfer rates; you’ll feel more confident when you locate a service provider in your area or you’re evaluating hosting services.