Privacy is becoming an increasingly prominent concern for us all. Until relatively recently, online privacy was a niche subject only of interest to academics and cybersecurity professionals. However, the explosion in popularity of social media and the growing influence that the biggest tech companies have over daily lives has bought the importance of digital privacy firmly into focus.
There are two main prongs to the current privacy debate. The first is the way that the custodians of our data, such as big social media and tech companies, conduct themselves. This is a complicated issue given that most of these businesses are based in the US but serve customers around the world.
The second prong of user privacy is the information that we willingly hand over and it is here that security researchers have been focusing their efforts. Understanding how and why your data might be misused will help you to make more informed decisions about what data you hand over to the businesses you use.
Malicious Apps

One of the best things about Android is that it is such an open operating system. Android gives you the ability to install apps from any source you choose. Google’s Play Store is curated, albeit not to the same degree as Apple’s App Store, so you can be confident that apps you download from there are unlikely to contain any malicious code, although the occasional malicious app does make it through.
Installing apps from unknown sources comes with its own risks, you should only do this if you trust the source or know the developer. However, even if you stick to downloading your apps from the Play Store, there is still a risk that you will be affected by malicious activity.
For example, many app developers make money by selling advertising space. When app developers do this, they rarely select the adverts themselves. Instead, they will use an existing code base provided by an advertiser that automatically serves ads to users. There are a number of ways that a malicious actor can hijack this advertising space for nefarious purposes.
Ad fraud is a growing issue among app developers. Not only are thieves making off with billions of dollars every year, but app developers and advertisers are also both losing out. Ad fraud can also harm the user themselves as adverts might be served that have malicious code or other hidden beacons and tags that can return personal data about the user.
Recommended for you: 5 Excellent Android Video Editing Apps You Should Consider.
IP Address

Before a device connects to the internet, it first needs to be assigned an IP address. Your internet service provider will automatically assign you an IP address to use when you are online. If you imagine yourself as a car, and the internet as a series of potential destinations all linked together by a super-fast highway, your IP address is like the license plate of the car. Not only is your IP address unique to the device you are using, but it can also reveal a lot of information about you. Most significantly, an IP address reveals your physical location.
Of course, the ability to trace an IP address back to a physical location depends on the skill and equipment available. Anyone with an internet connection can trace an IP address using countless services.
You might not think about your IP address as information that you are handing over. However, given that there are some simple steps you can take in order to keep your IP hidden and improve your privacy in general, you should consider whether you want anyone to know your IP address.
Securing Android

There are a number of things that you can do in order to improve your privacy on Android. First and foremost, think carefully before you provide any personal information to anyone. Ask yourself, is it necessary for them to have the information? Are you happy to hand it over or not? If you are in any doubt, it is better to err on the side of caution. If possible, find out how an entity plans to use your data before you give it to them.
There are some other simple steps you can take in order to better protect your data and the data stored on your device.
1. Set up a Proxy
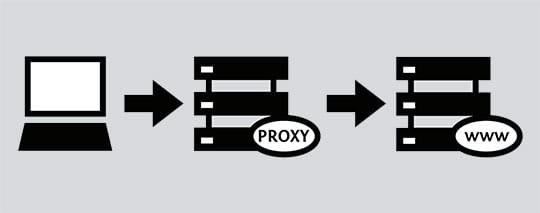
When you connect directly to a website or online service, your device connects to a physical server where the relevant data is stored. When you do this, your device tells the server its IP address. It means that whoever owns the server is able to see the IP addresses of anyone who connects to and uses the service.
A proxy server is a server that acts as a middleman between you and the server you want to connect to. Instead of connecting directly to the target server, your device will connect to the designated proxy server. When you load up a webpage, your device tells the proxy server what you want to do. The proxy server then connects to the target server and makes the request on your behalf. The target server sees the IP address of the proxy server, not your device.
A proxy server can, therefore, obscure your IP address and enhance your Android privacy. It can also be used to access region-locked content. For example, say you are located in the USA but your proxy server is located in Hong Kong; you will be able to surf the internet with a Hong Kong IP address. As far as any servers you connect to are concerned, you are in Hong Kong.
2. Update Everything

This is possibly the most important rule of good cybersecurity. Hackers are constantly looking for and finding new ways to undermine the security of Android, as well as individual apps. Most major phone manufacturers, as well as Google themselves, are good at responding promptly to major security issues. However, if you aren’t keeping your devices updated, you are doing the digital equivalent of not fixing a broken window.
You can set your device to automatically update itself, as well as individual apps, in your device settings. Unless you have a good and specific reason for not wanting to install an update, you should apply them as soon as they are available.
3. Use a Secure Messaging Platform

By default, most Android phones offer only a basic messaging app. If the manufacturer doesn’t have their own, like Samsung, they will usually default to Android Messages. You should look to replace this with an option that provides secure end-to-end encryption. WhatsApp is probably the most commonly used messaging app with E2E encryption. However, it is owned by Facebook, which has an awful reputation when it comes to data security and privacy.
We, therefore, recommend that you download Signal. The signal offers secure E2E encrypted messaging when both sender and receiver use the app. It can also send regular SMS to those who aren’t using Signal. This is better than WhatsApp, which can only communicate with other WhatsApp users.
Signal will also keep your unencrypted SMS messages stored in an encrypted database so they can’t be read by an intruder.
4. Delete Cookies

If you want to maintain privacy completely on your Android device, you should avoid logging into services that can personally identify you. If you are connecting with a VPN or proxy like Surfshark, there won’t be anything to identify the IP address you’re using as belonging to you. But, if you then log in to your Facebook account, the IP address you are using can now be tied to you as an individual.
When you log in to websites, a cookie is created for your session. These cookies can be used to track you and identify you. You should, therefore, clear out your cookies often. To do this, check the settings of your web browser. You can clear the caches of individual apps on your device. At first, long-press the app icon and then press the information button.
5. Avoid Apps You Don’t Trust

There are lots of really cool apps that aren’t available on the Play Store. However, you should always try and download your apps from either the Play Store or F-Droid. F-Droid is an unofficial app store that contains most of the most popular apps not available on the Play Store.
However, it is only apps from the official Play Store that should be considered safe. Anything else should be considered a potential threat until you know for sure what you are dealing with. Make sure to thoroughly investigate any app before downloading it. Using either the Play Store or F-Droid will enable you to download official. If you are downloading from the internet, you don’t know whether you are downloading the app or something pretending to be the app.
You may also like: 5 Privacy & Security Risks of Social Media & How to Prevent Those.
Final Words

Maintaining online privacy isn’t easy in the current ecosystem. Everyone is trying to get data from you, which they are then able to monetize. If you want to stay safe and private, you should invest in a proxy or VPN service (we recommend NordVPN). Also, make sure that you follow the tips outlined above.





