Microsoft Hyper-V is the virtualization platform that enables you to create and run virtual workloads on Windows OS. The most outstanding thing among all other Hyper-V features is the platform’s self-sufficiency. With Microsoft Hyper-V, you can create virtual machines (VMs) easily and quickly, as the feature does not need any supportive hardware or applications installed and synchronized.
With the release of Windows 11, many SMBs and enterprises, as well as individual users, upgraded their operating systems to the latest OS version by Microsoft. In this post, we will explain how to install Hyper-V on Windows 11. Or, to put it more accurately, show how to enable Hyper-V on Windows 11 systems.
Microsoft Windows Hyper-V System Requirements

Before we proceed to find out how to enable Hyper-V on the recently released Windows 11 OS, you should make sure that your hardware can provide enough performance to run Hyper-V VMs. The official system requirements to run the Hyper-V platform on Windows 11 are:
- OS: Windows 11 Pro, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise.
- CPU: 64-bit with Second Level Access Translation (SLAT).
- CPU support for VM Monitor Mode Extension (VT-x on Intel processors).
- 4 GB of RAM or more. VMs and the Hyper-V host share memory, so make sure you provide enough RAM for each new workload to run properly.
The requirements given by Microsoft are not high-level. Even home desktop or laptop systems can handle running some Hyper-V VMs if necessary. Still, high-performance hosts are required if you need to build a complex multi-level VM environment capable of providing services and running a stable production.
Recommended for you: How to Fix High RAM and CPU Usage in Windows 10?
Check BIOS settings for Hyper-V Support: Is Hardware Virtualization Enabled?
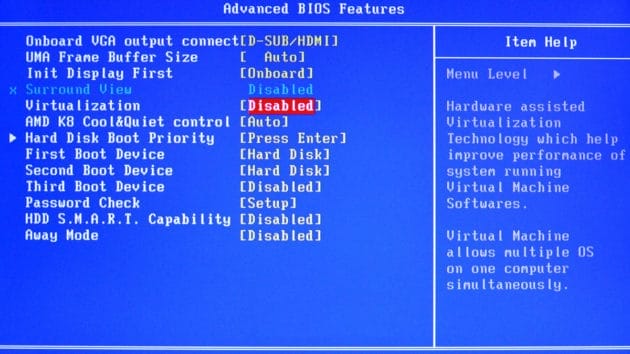
To create Hyper-V virtual machines, you need to enable Hardware Virtualization in the BIOS of your computer. Without this parameter enabled at the basic system level, you will not be able to enable Hyper-V on Windows 11.
To check and switch Hardware Virtualization parameters in BIOS, do the following:
- Power off your hardware, and then turn it back on (a standard OS reboot might suit most systems, too).
- Before the OS boots, enter the BIOS. Press the required key. For Asus motherboards, the key is usually “Delete” or “F2”, but your hardware may have different key bindings. Consult the hardware manual provided by the manufacturer to know the bindings for sure.
- Go through the BIOS menu tabs or use the UEFI search function to find the “Virtualization Technology (VTx)” option and enable the technology.
- Save the changes and exit BIOS settings.
- Then, the system will apply the changes, and your OS will boot regularly after that.
After the Hardware Virtualization is enabled in BIOS, your host’s hardware is ready to run Microsoft Windows Hyper-V VMs. However, the OS requires some additional internal tweaks.
Before You Start Building Your Hyper-V Environment

The importance of virtualized environments in the IT infrastructures of today’s SMBs and enterprises is hard to overestimate. Among other virtualization solutions, Microsoft Hyper-V enables the more efficient utilization of hardware resources and, therefore, optimized production. The VMs themselves and the data those VMs processes are critical to enable the stable functioning of the organization’s services and to ensure the technological existence of the organization.
The more important the data and VM infrastructure are, the more severe consequences an organization can expect in case of a disruptive event such as a ransomware attack, hardware failure, or natural disaster. The variety and danger of data loss threats continue to grow along with the increasing complexity of multileveled VM environments.
“The best way to protect Hyper-V VM infrastructure and data is to do regular backups. Plan your data protection strategy in advance. Picking a third-party backup and recovery solution can be the most efficient way to increase the resilience of your IT environment and ensure data availability even after major data loss disasters.” – as Bruce Talley, the CEO of Nakivo, suggested in one of his recent articles.
Install Hyper-V on Windows 11: Step-By-Step Guide

After you turn on the hardware virtualization in BIOS, you can enable Hyper-V on Windows 11 in three different ways. We will examine each way so you can get a clear view of the available tools.
Use Windows 11 Control Panel to Enable Hyper-V
Find the “Turn Windows features on or off” element via the Start menu search or the Control Panel tabs first to proceed with enabling Hyper-V on Windows 11. You’ll see the “Windows Features” window after clicking the relevant search result.
In that window, find the “Hyper-V” tab. Expand the available options by clicking on the plus pictogram nearby or double-clicking on the tab itself. After that, you’ll see two options with checkboxes appearing under the tab: “Hyper-V Management Tools” and “Hyper-V Platform”. Click on both checkboxes and hit the “OK” button below to save the changes you just made.
After that, the OS will display the progress of applying the changes. The entire process may take up to several minutes. A PC restart will be required once the process is complete. You can initiate a restart immediately by hitting the “Restart now” button. A shutdown can be avoided, if necessary, but the Hyper-V functionality will remain disabled until you allow the system to restart.
After the OS reboots, Microsoft Hyper-V will be enabled and ready to use. Access the feature to start creating your virtual workloads.
You may like: 25 Lesser-Known Amazing Windows 10 Features You Need to Know.
Enable Hyper-V via Command Prompt
The Command Prompt in the Windows Terminal is an option many prefer over the use of a regular interface when they need to enable OS features or services, including Hyper-V. The point is that the Command Prompt enables the streamlined and fast activation and management of Windows elements. Therefore, this way to enable Hyper-V on Windows 11 can be quicker than, for example, the use of the Control Panel. However, you need to know the required commands to use the Command Prompt efficiently.
First, open the Start Menu and use the search to find Windows Terminal. Run the Terminal as the administrator to get the required access and permissions.
The Windows Terminal application launches Windows PowerShell by default. Still, you can set the Command Prompt as the default launch option in the settings if necessary, or simply open the Command Prompt via the Terminal.
To open Command Prompt in the Windows Terminal, click on the arrow to the right from the new tab button in the upper part of the window. Then, choose the Command Prompt option in the displayed menu.
Now, you need to execute a single command. You can either type the command yourself or copy and paste it to the Command Prompt. The required command is:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName: Microsoft Hyper-VAfter typing or pasting the command, press Enter to execute it. The Command Prompt will then display the status of the feature activation. When the process is complete, the Command Prompt will display a message asking you about the Windows OS restart. If you want to restart the system instantly, press Y. If you need to postpone the OS restart, press N.
After the Windows 11 OS restarts, the Hyper-V feature is enabled, and you can start building your Hyper-V VM environment.

Windows PowerShell: Another Way to Enable Hyper-V
Shell commands in Windows PowerShell (wiki) are another thread to manage the system and run the required tasks in Windows 11. You can turn on Hyper-V with Windows PowerShell, too.
To enable Hyper-V with Windows PowerShell, use the search in the Start Menu to find and run the Windows Terminal. After the PowerShell tab is open, you’ll need to execute the following command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft Hyper-V -AllCopy or type the command in the PowerShell yourself, and press “Enter” to run the process.
A blue box with a progress bar will appear in the Windows PowerShell window to keep you updated about the status of the system changes to enable Hyper-V. The system will ask you about a restart after the Hyper-V feature has been enabled. To initiate the restart instantly, press Y. If you need the system to finish other tasks before the restart, you can postpone the restart by pressing N.
After the restart, the Hyper-V feature will be enabled in your Windows 11 system. Keep in mind that the restart may take a bit more time than usual because the system will need to apply the required changes before the OS boot.
You may also like: How to Stop Annoying Browser Notifications on a Windows 10 PC?
Conclusion

By default, the Hyper-V feature is disabled in Windows 11. To enable Hyper-V, you need to do the following steps:
- Ensure your hardware fulfills the system requirements.
- Enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS of your computer.
- Switch on Hyper-V via one of three tools (Control Panel, Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell).
- Reboot your system.
After these tweaks, the OS will enable Hyper-V and you’ll be able to create and run your VMs.